Kurdistan Province
Geography
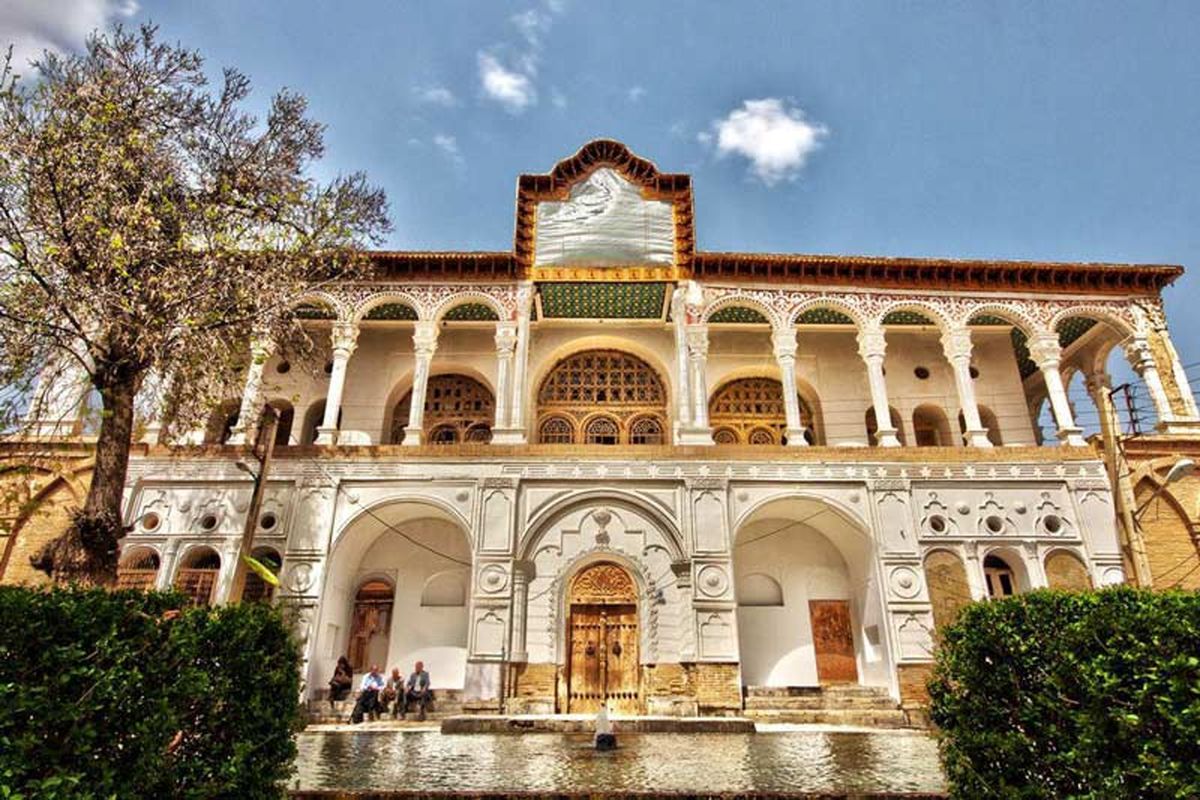
Kurdistan Province located in the northwestern part of Iran covers a wide geographic area (28,203 kilometers) and has over 200 kms of shared border with Iraqi Kurdistan. Its neighbouring provinces are West Azarbaijan (north) and Zanjan (north and east), Hamedan (east), Kermanshah (south) Based on the last official state divisions in 2003, the province consists of 9 cities, 23 towns, 23 districts, 79 rural districts and 1,767 villages. The capital of the province is Sanandaj which is 512 kilometers from Tehran. The major cities of this province are Baneh, Bijar, Diwandareh , Saqiz, Qorveh, Kamyaran, Sarvabad and Mariwan (see map). As per the last population census in 2003, Kurdistan Province has 1,574,119 inhabitants and the most populated cities being, in the order mentioned, Sanandaj (419,750 people) and Saghez.
Kurdistan
Natural and Climatic Conditions
Industry
Handicrafts
Kurdish Culture and Language
One of the most important attractions of the province is its cultural features such as language, ethnic music, ethnic costume, ethnic dance, festivals, celebrations, and handicrafts. People in this province speak Kurdish as their first language. The Kurdish language is a west Iranian language related to Farsi and Pashto and like Farsi is a branch of the Indo-European languages. It has its own grammatical and writing regulations as a language. Due to the sporadic dispersion of Kurdish population and the vastness of Kurdistan ("Land of the Kurds"), this language has two main dialects and some sub dialects. The existence of various dialects has made this language very rich in terms of the number of vocabularies; and the melodic tone of its vocabularies has tremendously enriched the literary and musical practices.
Kurdish dance or Halparkeh mirrors the past history of Kurdish people and by taking a closer look at Kurdish dance, we would find out that this art is a complete reflection of people's daily life and work. The roots of this art could be traced back into the people's religious beliefs, national festivals and celebrations, local games of war and defense, and inner feelings and moods. Kurdish dance has so many varieties throughout Kurdistan, but Sanandaj and Mariwan are two famous and rich cities in this regard and the varieties danced are named as follows: Garyan, Peshtpa, Halgerten, Fatah Pashayee, Chopi, Zangi, Shlan, Sehjar, and Khanameeri. Traditional musical instruments are still used for dancing to but modern electrical musical instruments are in wider use.
Kurdistan boasts one of the most beautiful costumes in the world. As it is written by many tourists in their travel books, Kurdish costumes are absolutely unique in terms of beauty, delicacy and color. Due to their positive attributes they have won the first place in several international festivals. Traditional Kurdish clothes are still widely used in everyday life in many parts of the province and gain special significance at weddings and religious ceremonies.